Hyperhidrosis, or excessive sweating, can be a source of both embarrassment and medical problems. Not only does it affect your social life, but it can also lead to physical problems that will hamper your quality of life. Fortunately, some effective treatments exist that can help manage or prevent hyperhidrosis.
What Is Excessive Hyperhidrosis?
The normal human body uses perspiration as a cooling mechanism when you are under strain. Like any bodily processes, the amount of sweating varies depending on how much you exert yourself or the situation. However, people with hyperhidrosis perspire more than normal. In some cases, they start perspiring more easily.
If you tend to sweat excessively with no specific stimuli, you may have hyperhidrosis. If you find yourself sweating profusely while in a cool room without having consumed any spicy foods, you are suffering from hyperhidrosis. Hyperhidrosis can be categorized into two main types. There is localized and generalized hyperhidrosis.
1. Localized Hyperhidrosis
It affects around three percent of the population, making it the most common type of hyperhidrosis. It is also known as primary focal hyperhidrosis. It is characterized by profuse perspiration in localized areas such as the armpits, hands, feet, groin or face. It is normally symmetrical, meaning it affects both sides of the body. However, there are some cases where may be asymmetrical, affect one side of the body.
Primary focal hyperhidrosis is considered a medical condition, not an illness. It may affect the quality of life, but it does not affect your health. When queried on the cause, most experts believe that it has neurological causes. They postulate that genetics may play a part in the propagation of the condition. There is currently no evidence that primary focal hyperhidrosis can cause medical complications. However, it is still a source of embarrassment for those diagnosed.
2. Generalized Hyperhidrosis
If you tend to have excessive perspiration throughout your entire body, you suffer generalized hyperhidrosis. Unlike localized hyperhidrosis, generalized hyperhidrosis is not limited to certain parts of the body. If you notice your swearing has abruptly become more profuse, this may be an indication that you have secondary generalized hyperhidrosis.
Unlike primary focal hyperhidrosis, secondary generalized hyperhidrosis is an indication that you are suffering from an underlying condition. An example is an increase in night sweats. This may develop with the onset of middle or old age. Secondary generalized hyperhidrosis may also be caused by ingestion of new medication.
If you have any symptoms like night sweats or an abrupt increase in perspiration, you should seek medical help. Make sure to carry a list of the medication that you may have taken in the past three months including supplements. A preliminary assessment will be done by your physicians to ascertain the cause of the sweating before the appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Steps in Treating Excessive Sweating
The first treatment a physician may prescribe is medical antiperspirants. They are somewhat different from the conventional deodorant because they contain aluminum salts that are useful in preventing perspiration. It works by spreading a thin film of aluminum salts on the skin. The salts block the sweat pores and stop sweating.
There are some that can be bought over the counter while others require a prescription. You should see a doctor when the over-the-counter antiperspirants no longer work. They can be applied to the armpits, the hands, feet, and even the hairline. Avoid the common mistake of only applying it in the morning. You should also apply it at night before going to bed.
Second Step : Home-Based Treatments
There are some home-based solutions that you can try to help reduce your excessive perspiration. A simple tip is to avoid wearing heavy clothes. Make sure you choose breathable fabrics as opposed to synthetic fabrics like nylon. You should carry an extra pair of clothes when you venture outside.
Make sure you use antibacterial soap when showering to kill bacteria on the skin that causes body odor. If your feet sweat a lot, try adding an extra inner sole that will absorb sweat and avoid odors. Do not forget to dry yourself completely before applying antiperspirant. This way, you will get the best results.
Third Step: Medical Treatment
If antiperspirants are not working, most dermatologists will probably suggest one of the following hyperhidrosis treatment methods:
1. Iontophoresis
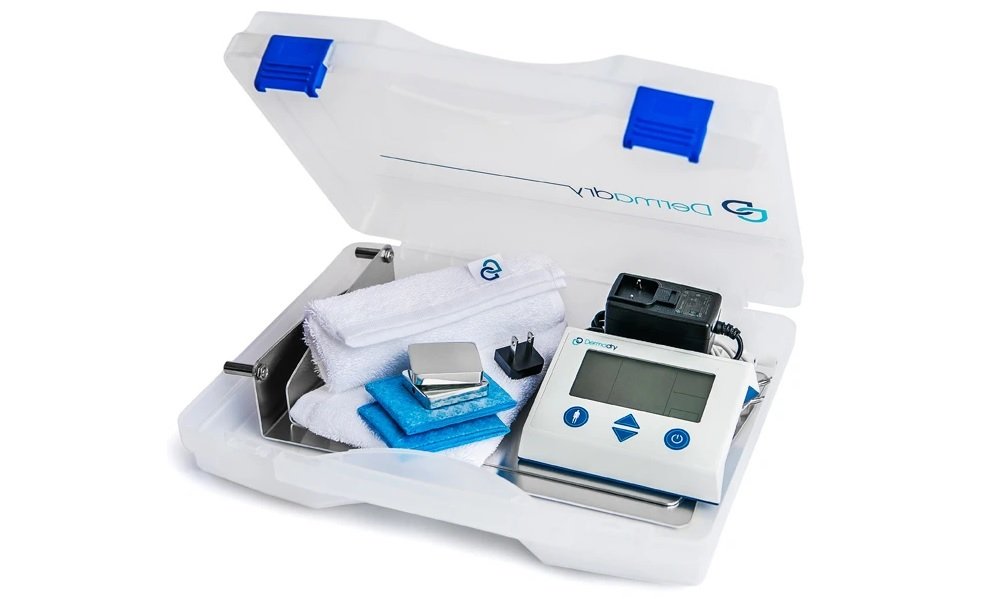
This is a hyperhidrosis treatment where the patient places the affected are in a low electric current. It is mainly used for those suffering from primary focal hyperhidrosis, especially of the feet and hands. There are now many iontophoresis machines including the Dermadry, which can actually be used at your own home.
Dermatologists believe that the electric current forcefully blocks the sweat pores preventing excessive perspiration.
It is a relatively safe process, and most patients report a substantial decrease in sweat production after a month of two. However, since the machines use electric current, pregnant women or people with metal implants should avoid iontophoresis machines.
2. Botox injections
If iontophoresis is not effective or it cannot be used, as in the case of underarm sweat, your physician may prescribe Botox injections. Botox is the injection of chemicals into the dermal layer of your skin to block the sweat pores. As scary as it may seem, this is an FDA-approved procedure for dealing with excessive sweating. The results of Botox injections are normally long term. You may be sweat free for around a year when done right.
3. Anticholinergic treatment
This is a hyperhidrosis treatment that involves oral ingestion of prescription medication. It is the next option when Botox and iontophoresis no longer work. The anticholinergic treatments chemically and hormonally impair how sweat glands work. However, such treatments may cause side effects like cardiac palpitations, urinary problems, migraines and blurred vision
4. Surgery
If the patient is unable to cope with the anticholinergic treatments, the last resort is dermatological surgery.
Due to the intrusive nature of surgical procedures, this option should only be used by people suffering from severe hyperhidrosis. It can be done in two ways. In the first method, the plastic surgeon cuts or scrapes out the sweat glands.
The alternative is a procedure known as ETS (endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy). Instead of the surgeon cutting the sweat glands directly, he cuts the nerves underneath the sweat glands. Even though this is normally an effective treatment, it should only be used when all other treatments fail. It is irreversible, and you will have scars for the rest of your life. ETS may have some adverse side effects like compensatory perspiration. This is when your body sweats in an unusual area, like the chest or face, to compensate for the impaired sweating in the area you had surgery.
Medical Problems Associated with Hyperhidrosis
Those who suffer from excessive perspiration feel embarrassed and inconvenienced by the condition. They are unable to have an optimal quality of life, and they are filled with anxiety. Apart from the psychological impact, excessive perspiration may be an indication of underlying medical complications. It is a common symptom for those with thyroid issues, diabetes or undiagnosed infections. You are also likely to sweat more when you are overweight or obese. If you notice that your sweating has become more profuse, book an appointment with a physician or dermatologist.











